Table of Contents
What is NPT ?
NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered Threads. American National Standard Pipe Thread is often called NPT (National Pipe Tapered Threads) for short. Under NPT, the pipe should be threaded as per ANSI B1.20.1. It is US national technical standard used for measuring tapered screw threads on pipes and fittings.
Please note, NPT threads are not interchangeable with NPS (National Pipe Straight) threads. The threads in NPT are tapered whereas threads in NPS are straight. Taper threads provide much effective sealing than straight threads. The flanks of NPT threads compress against each other and thereby forming a seal.
Therefore, NPT threads are most commonly used in transporting liquids, gases, chemicals, steam and hydraulic fluids.
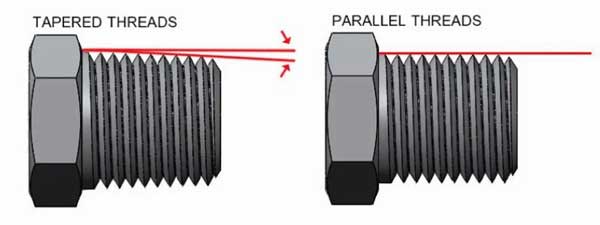
Characteristics of NPT
- NPT threads taper at a rate of 3/4″ per feet or 62.5mm/mtr
- Larger diameter keeps compressing on smaller diameter and therefore forming a seal
- Threads have an included angle of 60°
- No clearance remains between the root and crest of the threads
- The angle between taper and center axis of is 1.7899° or 1°47’24”
However, NPT threads are not completely leak-proof. There are a number of reasons that can cause leakages. It is highly advisable to apply aa sealant on the threads before use.
Leakage Causes & Precautions
NPT threads were initially designed for water pipe plumbing applications with a working pressure of 60 psi. These threads are generally not recommend for high pressure applications as they tend to leak more often compared to their counterparts.
Causes
- Thread designs is meant to form a seal and therefore, precision is of utmost important
- Under tightened connection
- Over tightened connection
- Poor lubrication
These are some of the reasons that can cause leakages in NPT threads.
Precautions
As we see that tightening of the thread can become a problem. Under and over tightening is a issue constantly faced. However, there is no such standard where we can safely say that these measures can help with the task. Provided the fact that with every use, the threads are also subject to wear and tear.
The best precaution is applying sealant. The sealant on the thread prevent it from leaking but also keep in mind the tightening requirements as it depends on the type of sealant. One such sealant that is used for such an application is PTFE tape (also known as teflon tape).

Difference Between NPT and NPTF
NPT = National Pipe Taper Thread (ANSI B1.20.1)
NPTF = National Pipe Taper Thread Fuel (ANSI B1.20.3)
NTPF threads are designed to provide a more leak-free seal without the use of PTFE tapes / teflon tapes or any other sealant. The difference between the NPT and NPTF threads lies in the root and crest of the threads.
Though the shape of NPT and NPTF threads is the same, NPTF root and crest heights are adjusted for an interference fit which creates a mechanical seal through thread form deformation at assembly.
NPT and NPTF both have screw thread design but NPT needs a sealant to be leak-free whereas NPTF does not necessarily require a sealant to be leak-free. NPTF threads are best suited for liquid, gases, chemical, steam, oil and hydraulic purposes.

NPT Technical Specification
| Nominal Pipe Size | Thread Density | Thread Pitch | Thread Length | Overall Length | Thread Diameter | Outside Diameter |
| 1/16 | 27 | 0.03703 | 0.2611 | 0.3896 | 0.2875 | 0.313 |
| 1/8 | 27 | 0.03703 | 0.2639 | 0.3924 | 0.38000 | 0.405 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 0.05555 | 0.4018 | 0.5946 | 0.50250 | 0.540 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 0.05555 | 0.4078 | 0.6006 | 0.63750 | 0.675 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 0.07142 | 0.5337 | 0.7815 | 0.79178 | 0.840 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 0.07142 | 0.5457 | 0.7935 | 1.00178 | 1.050 |
| 1 | 11.1/2 | 0.08695 | 0.6828 | 0.9845 | 1.25631 | 1.315 |
| 1.1/4 | 11.1/2 | 0.08695 | 0.7068 | 1.0085 | 1.60131 | 1.660 |
| 1.1/2 | 11.1/2 | 0.08695 | 0.7235 | 1.0252 | 1.84131 | 1.900 |
| 2 | 11.1/2 | 0.08695 | 0.7565 | 1.0582 | 2.31630 | 2.375 |
| 2.1/2 | 8 | 0.12500 | 1.1375 | 1.5712 | 2.79063 | 2.875 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.12500 | 1.2000 | 1.6337 | 3.41563 | 3.500 |
| 3.1/2 | 8 | 0.12500 | 1.2500 | 1.6837 | 3.91563 | 4.000 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.12500 | 1.3000 | 1.7337 | 4.41563 | 4.500 |
Check out our complete range of hose end fittings. We offer an expansive product selection, quality and reliability.
